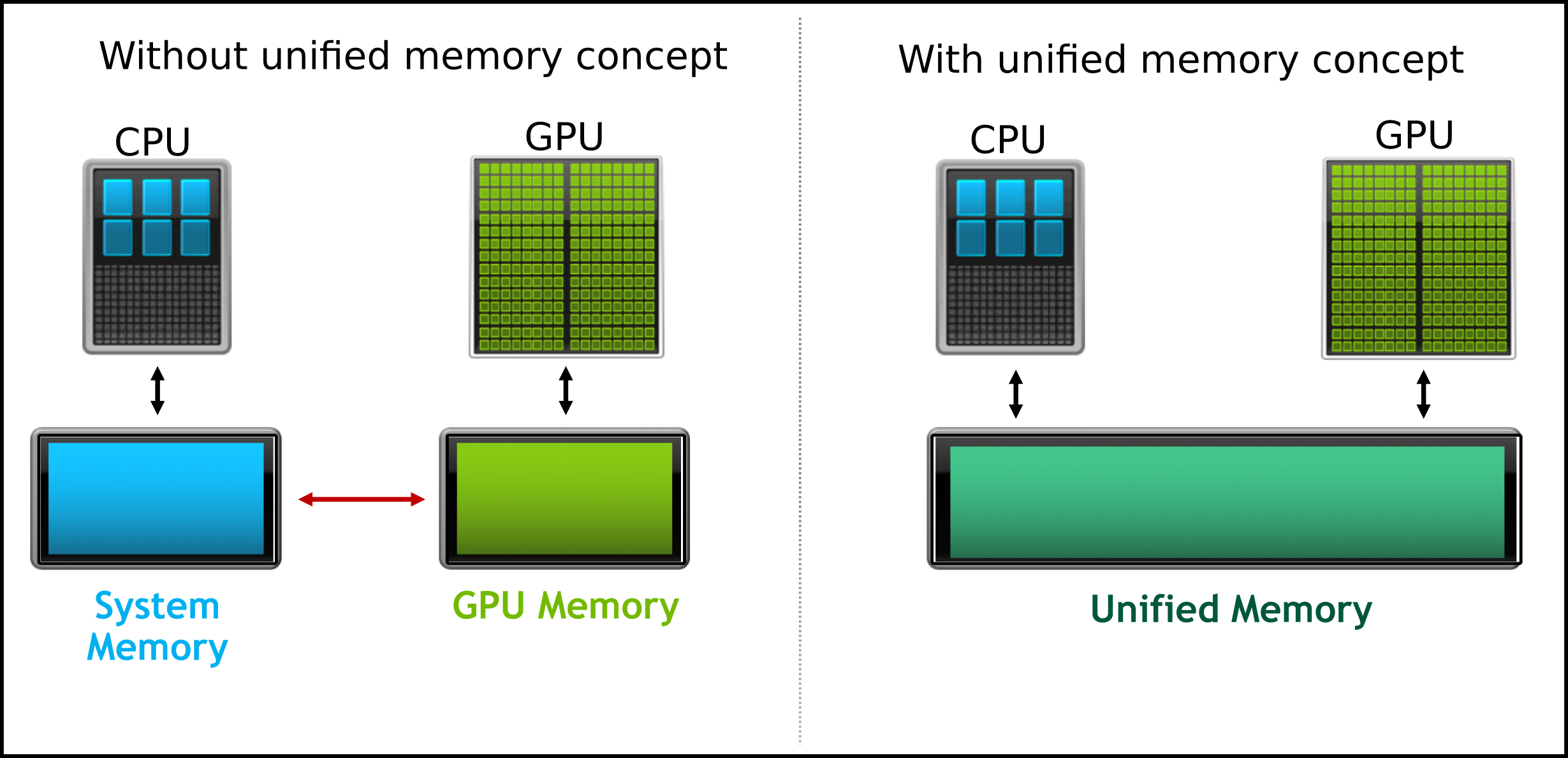
Unified Memory
Unified memory streamlines the data transfer process between the host (CPU) and the device (GPU), minimizing the need for explicit data movement by programmers. The CUDA API facilitates this data management, effectively handling the transfer of data between the CPU and GPU. In this tutorial, we will explore the concept of unified memory through a practical example of vector addition performed on the GPU.
- Just one memory allocation is enough
cudaMallocManaged(). The table below summarises the required steps needed for the unified memory concept.
| Without unified memory | With unified memory |
|---|---|
| Allocate the host memory | |
| Allocate the device memory | Allocate the device memory |
| Initialize the host value | Initialize the host value |
| Transfer the host value to the device memory location | |
| Do the computation using the CUDA kernel | Do the computation using the CUDA kernel |
| Transfer the data from the device to host | |
| Free device memory | Free device memory |
| Free host memory |
Questions and Solutions¶
Examples: Unified Memory - Vector Addition
//-*-C++-*-
// Without-unified-memory.cu
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
#define N 5120
#define MAX_ERR 1e-6
// GPU function that adds two vectors
__global__ void vector_add(float *a, float *b,
float *out, int n)
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x * blockDim.y +
threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// Allow the threads only within the size of N
if(i < n)
{
out[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
// Synchronize all the threads
__syncthreads();
}
int main()
{
// Initialize the memory on the host
float *a, *b, *out;
// Allocate host memory
a = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
b = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
c = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
// Initialize the memory on the device
float *d_a, *d_b, *d_out;
// Allocate device memory
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_a, sizeof(float) * N);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_b, sizeof(float) * N);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_out, sizeof(float) * N);
// Initialize host arrays
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
a[i] = 1.0f;
b[i] = 2.0f;
}
// Transfer data from a host to device memory
cudaMemcpy(d_a, a, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_b, b, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Thread organization
dim3 dimGrid(ceil(N/32), ceil(N/32), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(32, 32, 1);
// Execute the CUDA kernel function
vector_add<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_a, d_b, d_out, N);
// Transfer data back to host memory
cudaMemcpy(out, d_out, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Verification
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
assert(fabs(out[i] - a[i] - b[i]) < MAX_ERR);
}
printf("out[0] = %f\n", out[0]);
printf("PASSED\n");
// Deallocate device memory
cudaFree(d_a);
cudaFree(d_b);
cudaFree(d_out);
// Deallocate host memory
free(a);
free(b);
free(out);
return 0;
}
//-*-C++-*-
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
#define N 5120
#define MAX_ERR 1e-6
// GPU function that adds two vectors
__global__ void vector_add(float *a, float *b,
float *out, int n)
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x * blockDim.y +
threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// Allow the threads only within the size of N
if(i < n)
{
out[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
// Synchronize all the threads
__syncthreads();
}
int main()
{
/*
// Initialize the memory on the host
float *a, *b, *out;
// Allocate host memory
a = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
b = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
c = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
*/
// Initialize the memory on the device
float *d_a, *d_b, *d_out;
// Allocate device(unified) memory
cudaMallocManaged......
// Initialize host arrays
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
d_a[i] = ...
d_b[i] = ...
}
/*
// Transfer data from a host to device memory
cudaMemcpy(d_a, a, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_b, b, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
*/
// Thread organization
dim3 dimGrid...
dim3 dimBlock...
// execute the CUDA kernel function
vector_add<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_a, d_b, d_out, N);
// synchronize if needed
......
/*
// Transfer data back to host memory
cudaMemcpy(out, d_out, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
*/
// Verification
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
assert(fabs(d_out[i] - d_a[i] - d_b[i]) < MAX_ERR);
}
printf("out[0] = %f\n", d_out[0]);
printf("PASSED\n");
// Deallocate device(unified) memory
cudaFree...
/*
// Deallocate host memory
free(a);
free(b);
free(out);
*/
return 0;
}
//-*-C++-*-
// With-unified-memory.cu
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
#define N 5120
#define MAX_ERR 1e-6
// GPU function that adds two vectors
__global__ void vector_add(float *a, float *b,
float *out, int n)
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x * blockDim.y +
threadIdx.y * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// Allow the threads only within the size of N
if(i < n)
{
out[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
// Synchronize all the threads
__syncthreads();
}
int main()
{
/*
// Initialize the memory on the host
float *a, *b, *out;
// Allocate host memory
a = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
b = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
c = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * N);
*/
// Initialize the memory on the device
float *d_a, *d_b, *d_out;
// Allocate device memory
cudaMallocManaged(&d_a, sizeof(float) * N);
cudaMallocManaged(&d_b, sizeof(float) * N);
cudaMallocManaged(&d_out, sizeof(float) * N);
// Initialize host arrays
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
d_a[i] = 1.0f;
d_b[i] = 2.0f;
}
/*
// Transfer data from a host to device memory
cudaMemcpy(d_a, a, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_b, b, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
*/
// Thread organization
dim3 dimGrid(ceil(N/32), ceil(N/32), 1);
dim3 dimBlock(32, 32, 1);
// Execute the CUDA kernel function
vector_add<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_a, d_b, d_out, N);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
/*
// Transfer data back to host memory
cudaMemcpy(out, d_out, sizeof(float) * N, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
*/
// Verification
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
assert(fabs(d_out[i] - d_a[i] - d_b[i]) < MAX_ERR);
}
printf("out[0] = %f\n", d_out[0]);
printf("PASSED\n");
// Deallocate device memory
cudaFree(d_a);
cudaFree(d_b);
cudaFree(d_out);
/*
// Deallocate host memory
free(a);
free(b);
free(out);
*/
return 0;
}
Compilation and Output
Questions
- Here in this example, we have used
cudaDeviceSynchronize(); can you removecudaDeviceSynchronize()and still get a correct solution? If not, why (think)? - Please try using different thread blocks and array sizes.
Last update: January 20, 2025 18:42:10
Created: March 11, 2023 20:16:27
Created: March 11, 2023 20:16:27